11. ch01. matplotlib - 11. histogram - 15. ch01. matplotlib - 15. imshow
5. Histogram
5-1. 기본 Histogram 그리기
N = 100000
bins = 30
x = np.random.randn(N)
plt.hist(x, bins=bins)
plt.show()
5-2. 다중 Histogram
sharey: y축을 다중 그래프가 share
tight_layout: graph의 패딩을 자동으로 조절해주어 fit한 graph를 생성
N = 100000
bins=30
x = np.random.randn(N)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3,
sharey=True,
tight_layout=True
)
fig.set_size_inches(12,5)
axs[0].hist(x, bins=bins)
axs[1].hist(x, bins=bins*2)
axs[2].hist(x, bins=bins*4)
plt.show()
5-3. Y축에 Density
N = 100000
bins = 30
x = np.random.randn(N)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2,
tight_layout=True
)
fig.set_size_inches(9, 3)
axs[0].hist(x, bins=bins, density = True, cumulative=True) 누적분포 볼 때 cumulative
axs[1].hist(x, bins=bins*2, density = True)
density = True
# density=True 값을 통하여 Y축에 density를 표기할 수 있습니다.
plt.show()
12. ch01. matplotlib - 12. pie chart
6. Pie Chart
점유율
pie chart 옵션
explode: 파이에서 툭 튀어져 나온 비율
autopct: 퍼센트 자동으로 표기
shadow: 그림자 표시
startangle: 파이를 그리기 시작할 각도
texts, autotexts 인자를 리턴 받습니다.
texts는 label에 대한 텍스트 효과를
autotexts는 파이 위에 그려지는 텍스트 효과를 다룰 때 활용
너무 인자가 많을 때는 barchart 사용
labels = ['Samsung', 'Huawei', 'Apple', 'Xiaomi', 'Oppo', 'Etc']
sizes = [20.4, 15.8, 10.5, 9, 7.6, 36.7]
explode = (0.3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
# texts, autotexts 인자를 활용하여 텍스트 스타일링을 적용합니다
patches, texts, autotexts = plt.pie(sizes,
explode=explode,
labels=labels,
autopct='%1.1f%%',
shadow=True,
startangle=90
)
plt.title('Smartphone pie', fontsize=15)
# label 텍스트에 대한 스타일 적용
for t in texts:
t.set_fontsize(12)
t.set_color("gray")
# pie 위의 텍스트에 대한 스타일 적용
for t in autotexts:
t.set_color("white")
t.set_fontsize(18)
plt.show()
13. ch01. matplotlib - 13. boxplot
# 샘플 데이터 생성
spread = np.random.rand(50) * 100
center = np.ones(25) * 50
flier_high = np.random.rand(10) * 100 + 100
flier_low = np.random.rand(10) * -100
data = np.concatenate((spread, center, flier_high, flier_low)
7-1. 기본 박스플롯
plt.boxplot(data)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
7-2. 다중 박스플롯 생성
# 샘플 데이터 생성
spread = np.random.rand(50) * 100
center = np.ones(25) * 50
flier_high = np.random.rand(10) * 100 + 100
flier_low = np.random.rand(10) * -100
data = np.concatenate((spread, center, flier_high, flier_low))
spread = np.random.rand(50) * 100
center = np.ones(25) * 40
flier_high = np.random.rand(10) * 100 + 100
flier_low = np.random.rand(10) * -100
d2 = np.concatenate((spread, center, flier_high, flier_low))
data.shape = (-1, 1)
d2.shape = (-1, 1)
data = [data, d2, d2[::2,0]]
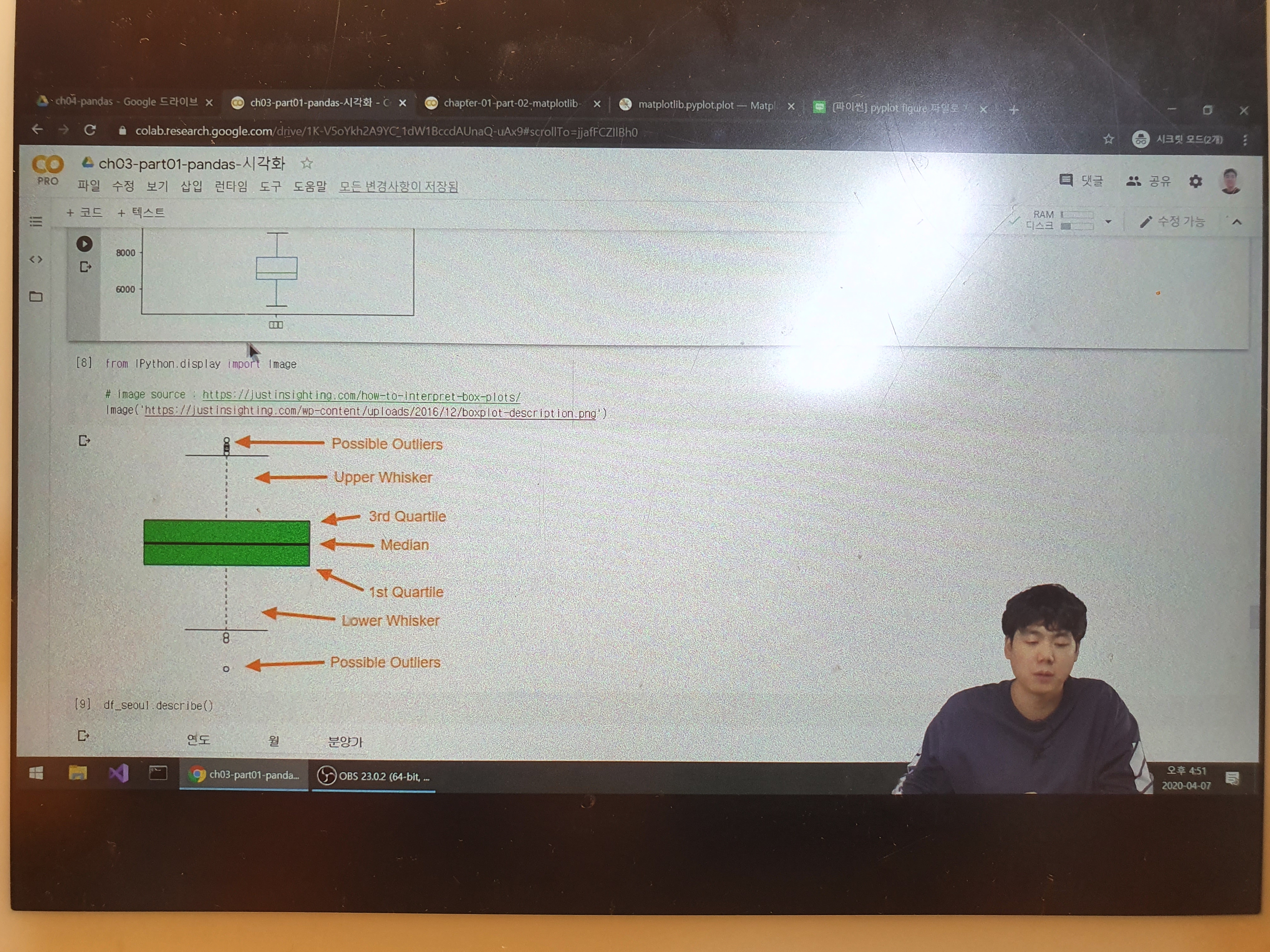
boxplot()으로 매우 쉽게 생성할 수 있습니다.
다중 그래프 생성을 위해서는 data 자체가 2차원으로 구성되어 있어야 합니다.
row와 column으로 구성된 DataFrame에서 Column은 X축에 Row는 Y축에 구성된다
plt.boxplot(data)
plt.show()
7-3. Box Plot 축 바꾸기
vert=False 옵션을 통해 표시하고자 하는 축을 바꿀 수 있습니다.
plt.title('Horizontal Box Plot', fontsize=15)
plt.boxplot(data, vert=False)
plt.show()
7-4. Outlier 마커 심볼과 컬러 변경
outlier_marker = dict(markerfacecolor='r', marker='D')
plt.title('Changed Outlier Symbols', fontsize=15)
plt.boxplot(data, flierprops=outlier_marker)
plt.show()
14. ch01. matplotlib - 14. 3d 시각화
8. 3D 그래프 그리기
mplot3d를 추가로 import
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d 외울필요 X
데이터 분석을 위해서는 2차원이 더 좋음.
8-1. 밑그림 그리기 (캔버스)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
8-2. 3d plot 그리기
# project=3d로 설정합니다
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
# x, y, z 데이터를 생성합니다
z = np.linspace(0, 15, 1000)
x = np.sin(z)
y = np.cos(z)
ax.plot(x, y, z, 'gray')
plt.show()
# project=3d로 설정합니다
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
sample_size = 100
x = np.cumsum(np.random.normal(0, 1, sample_size))
y = np.cumsum(np.random.normal(0, 1, sample_size))
z = np.cumsum(np.random.normal(0, 1, sample_size))
ax.plot3D(x, y, z, alpha=0.3, marker='*')
plt.title("ax.plot")
plt.show()
ax.plot 이거나 ax.plot3D
8-3. 3d-scatter 그리기
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') # Axe3D object
sample_size = 500
x = np.cumsum(np.random.normal(0, 5, sample_size))
y = np.cumsum(np.random.normal(0, 5, sample_size))
z = np.cumsum(np.random.normal(0, 5, sample_size))
ax.scatter(x, y, z, c = z, s=20, alpha=0.5, cmap='Greens')
plt.title("ax.scatter")
plt.show()
8-4. contour3D 그리기 (등고선)
x = np.linspace(-6, 6, 30)
y = np.linspace(-6, 6, 30)
x, y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
z = np.sin(np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.contour3D(x, y, z, 20, cmap='Reds')
plt.title("ax.contour3D")
plt.show()
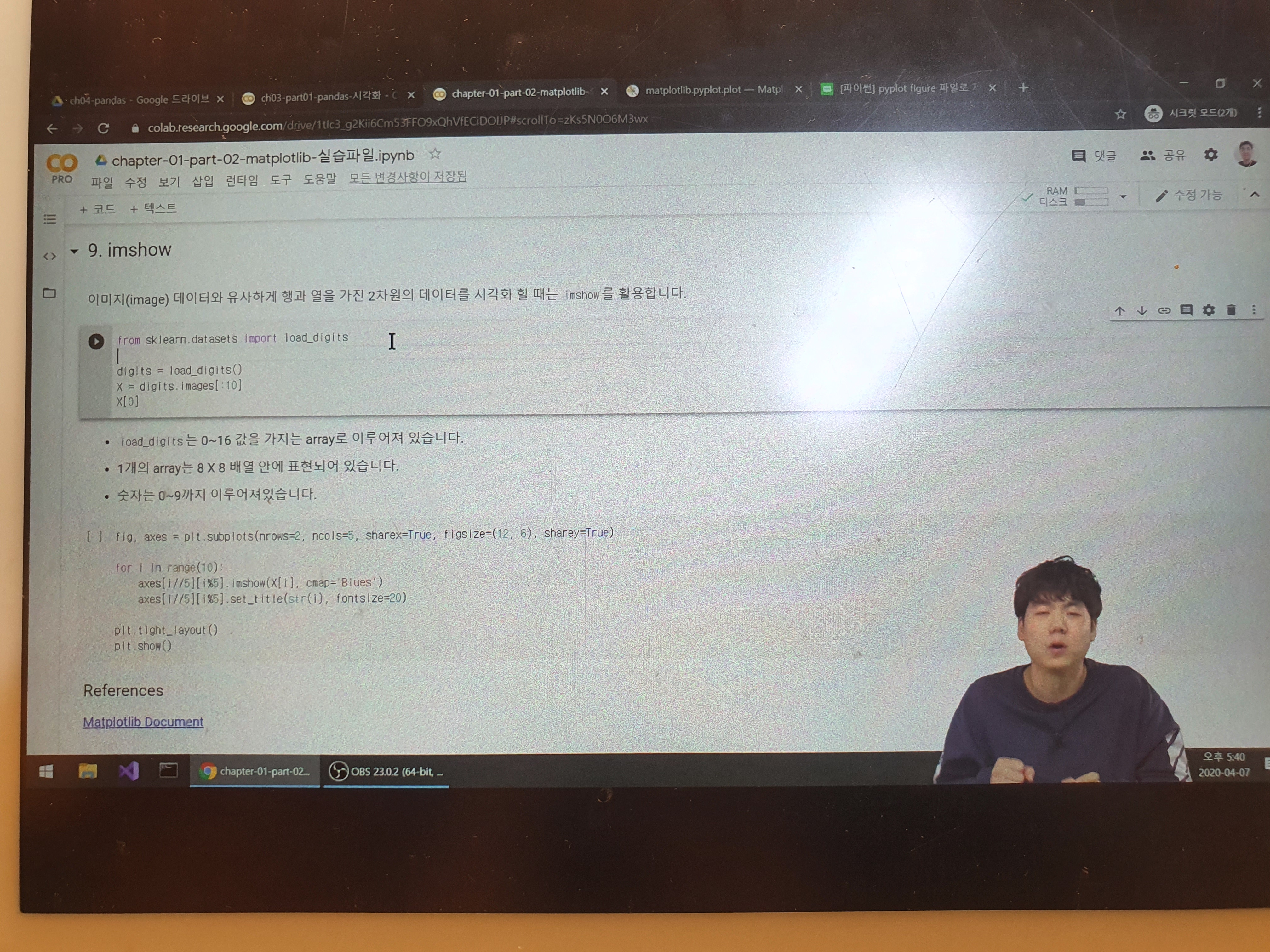
15. ch01. matplotlib - 15. imshow
9. imshow
이미지(image) 데이터와 유사하게 행과 열을 가진 2차원의 데이터를 시각화 할 때는 imshow를 활용
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.images[:10]
X[0]
load_digits는 0~16 값을 가지는 array로 이루어져 있습니다.
1개의 array는 8 X 8 배열 안에 표현되어 있습니다.
숫자는 0~9까지 이루어져있습니다.
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=5, sharex=True, figsize=(12, 6), sharey=True)
for i in range(10):
axes[i//5][i%5].imshow(X[i], cmap='Blues')
axes[i//5][i%5].set_title(str(i), fontsize=20)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
패스트캠퍼스 데이터분석 강의 링크
bit.ly/3imy2uN